-
Products
-
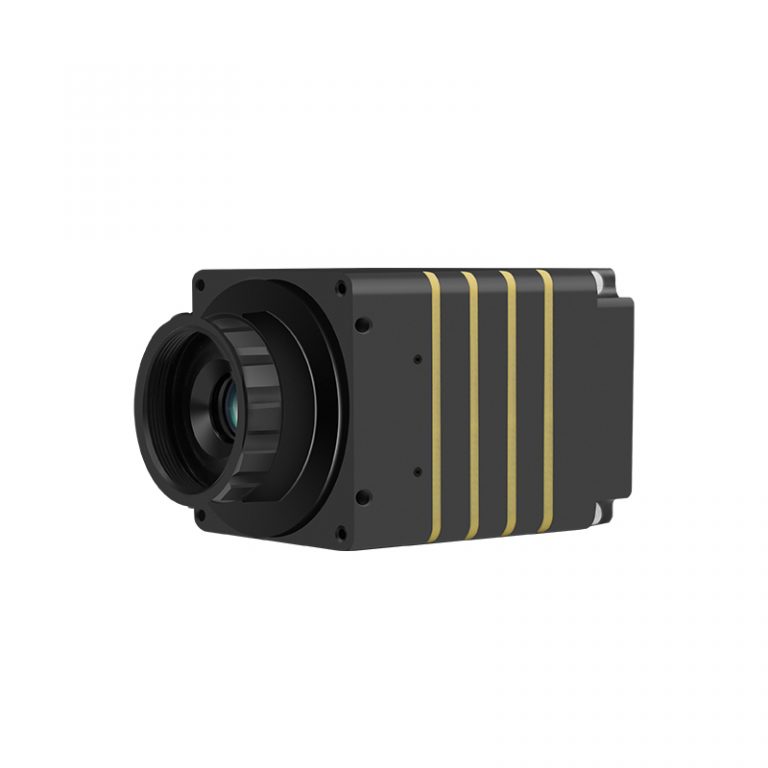

Infrared Thermal Camera Module-
-
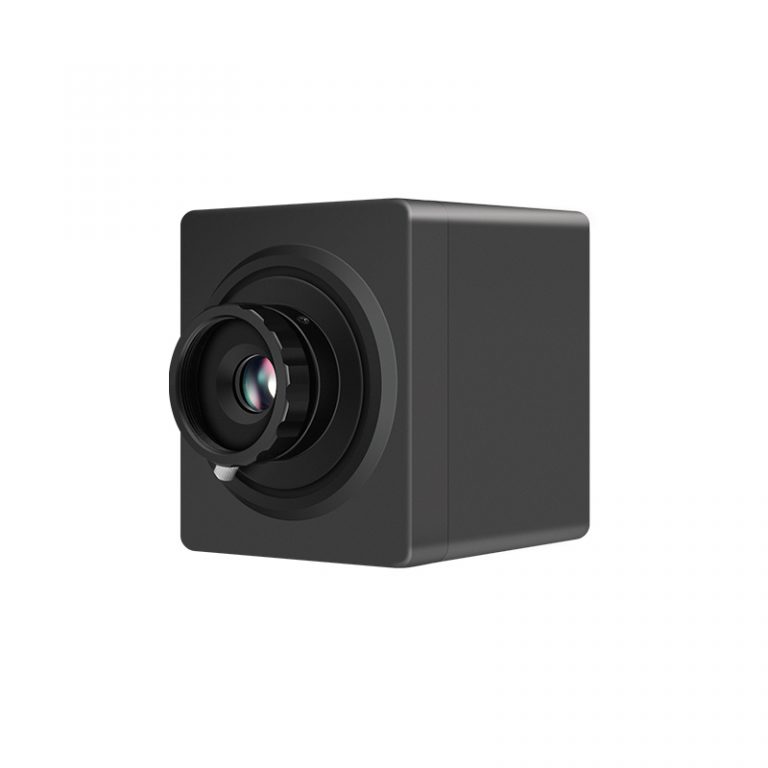

On-line Temperature Measuring T
-
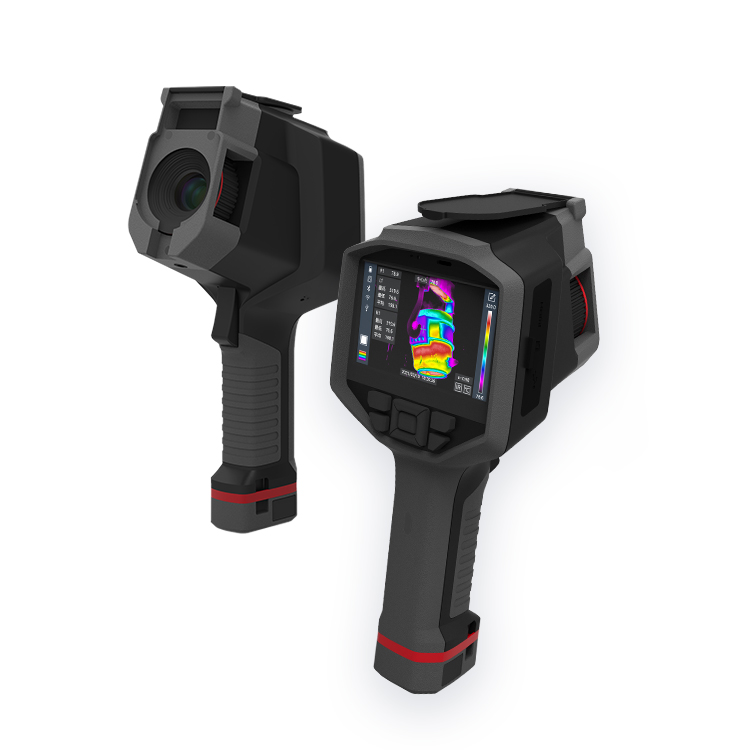

Professional Handheld Thermal C
-
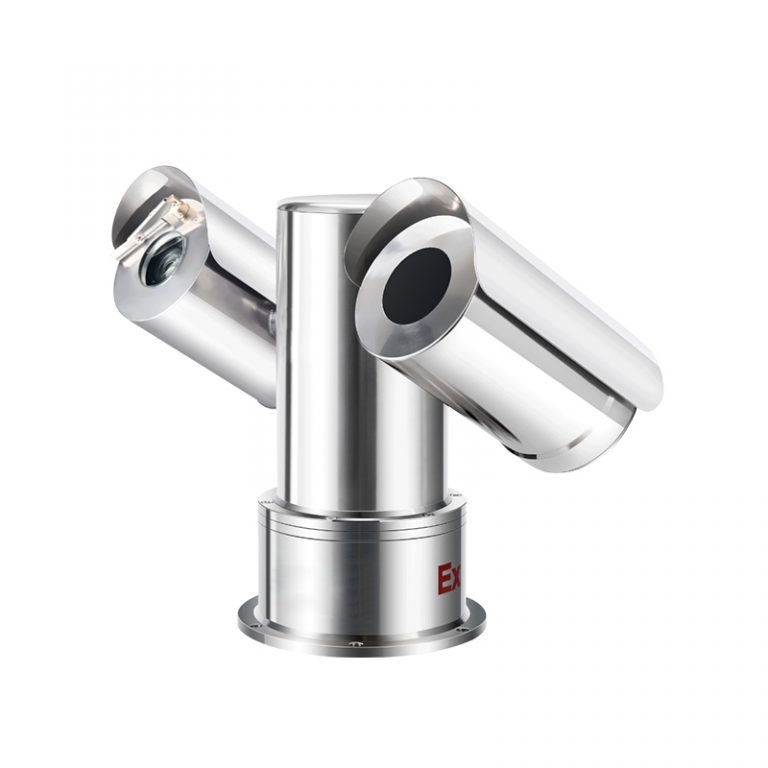

Bi-Spectrum Explosion-proof The
-
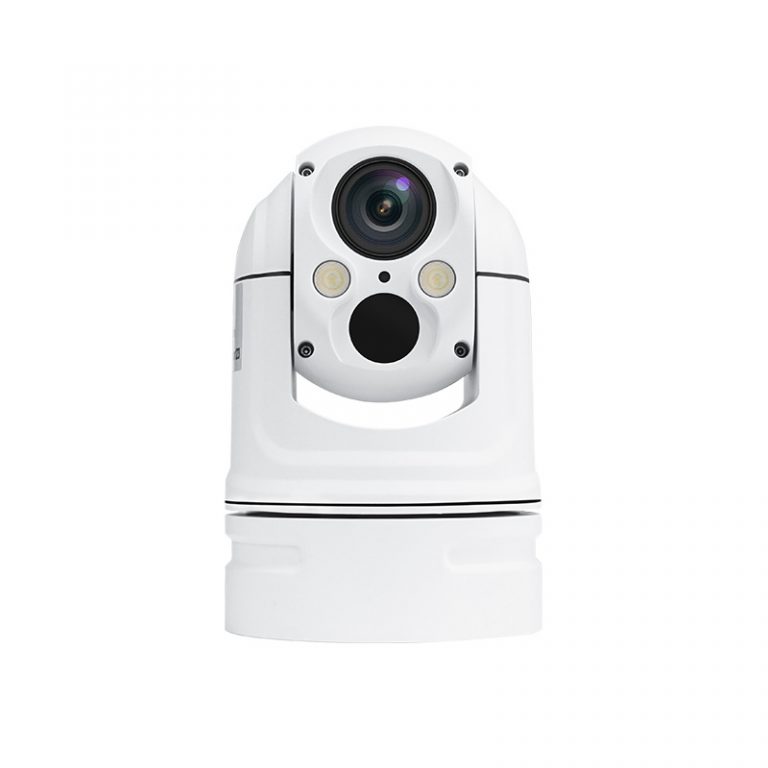

Small Bi-Spectrum Globular Ther
-
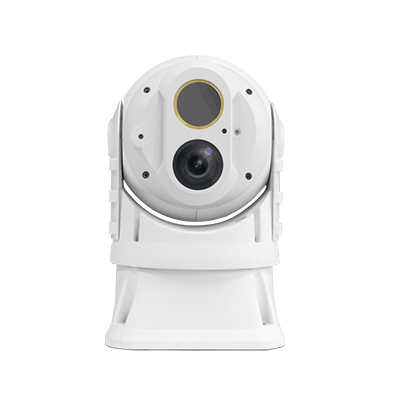

Big Bi-Spectrum Globular Therma
-
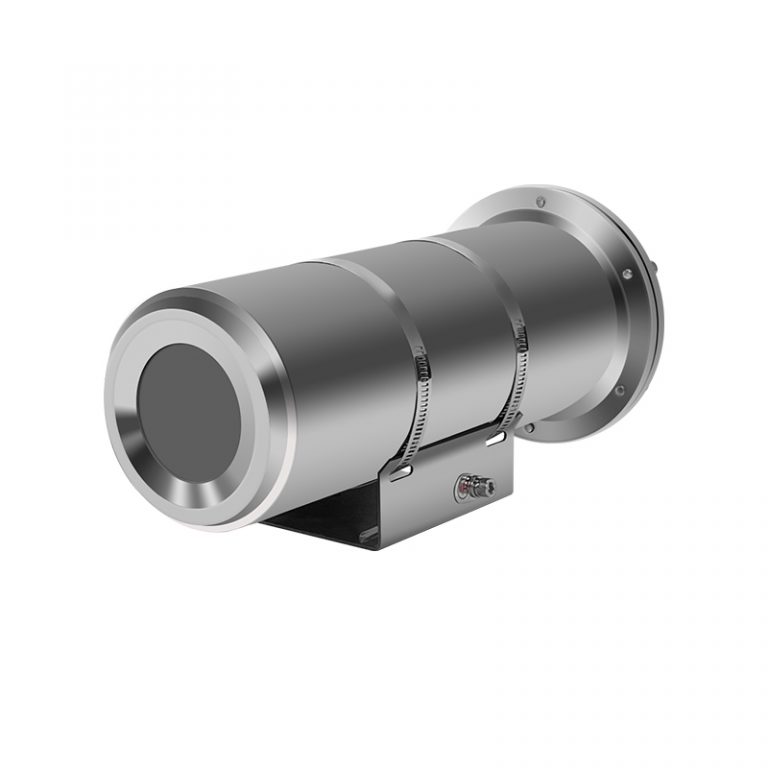

Monocular Explosion-proof Therm
-
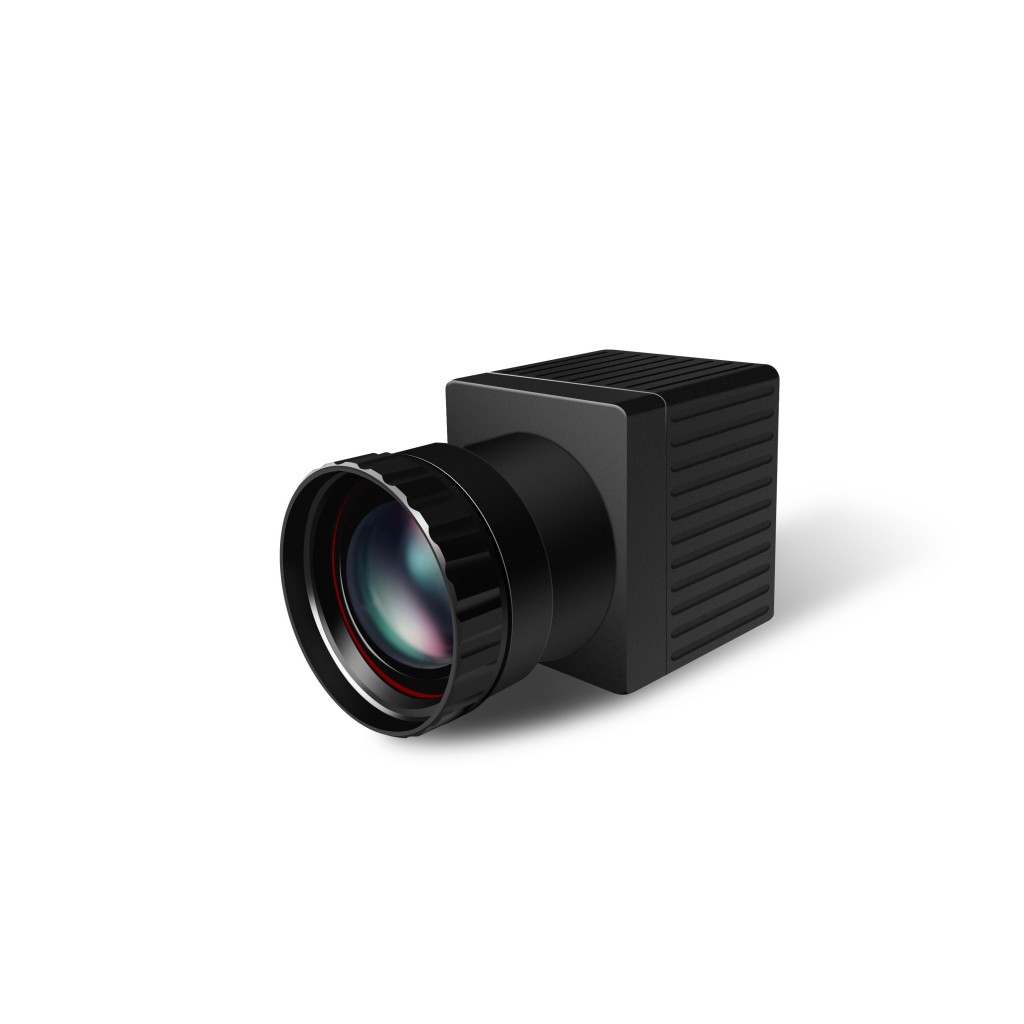

Yoseen Infrared Thermal Camera
-
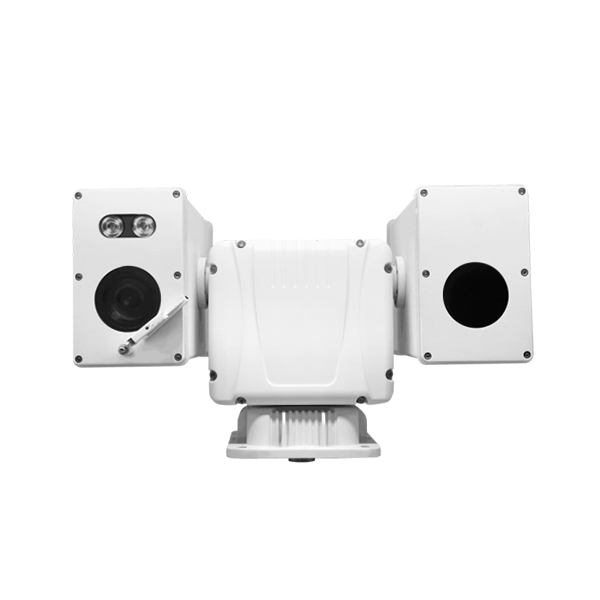

Bi-Spectrum Thermal T-Camera
-
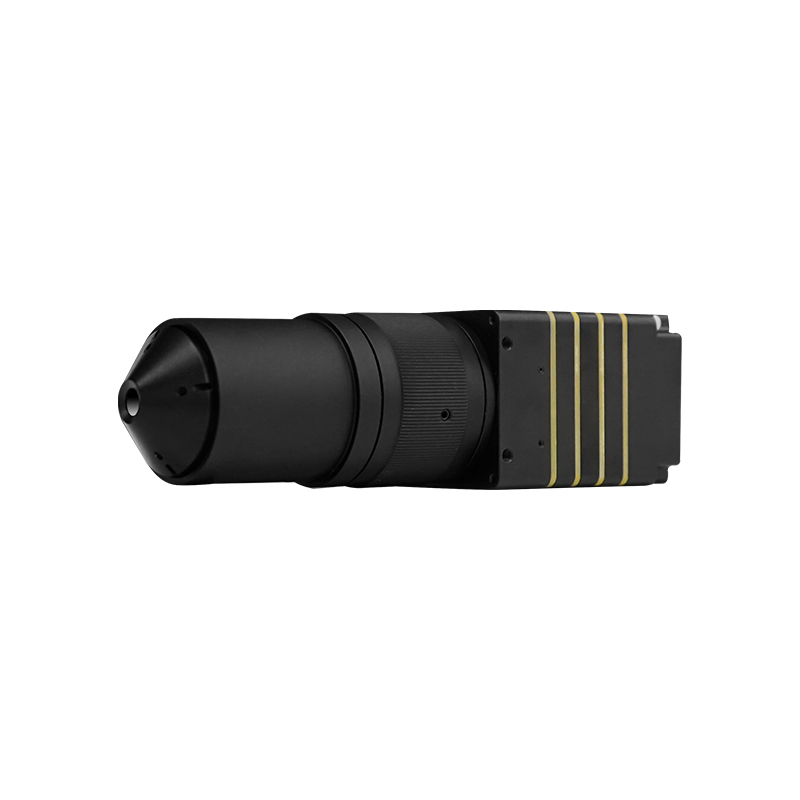

Blast Furnace Monitoring Therma
-
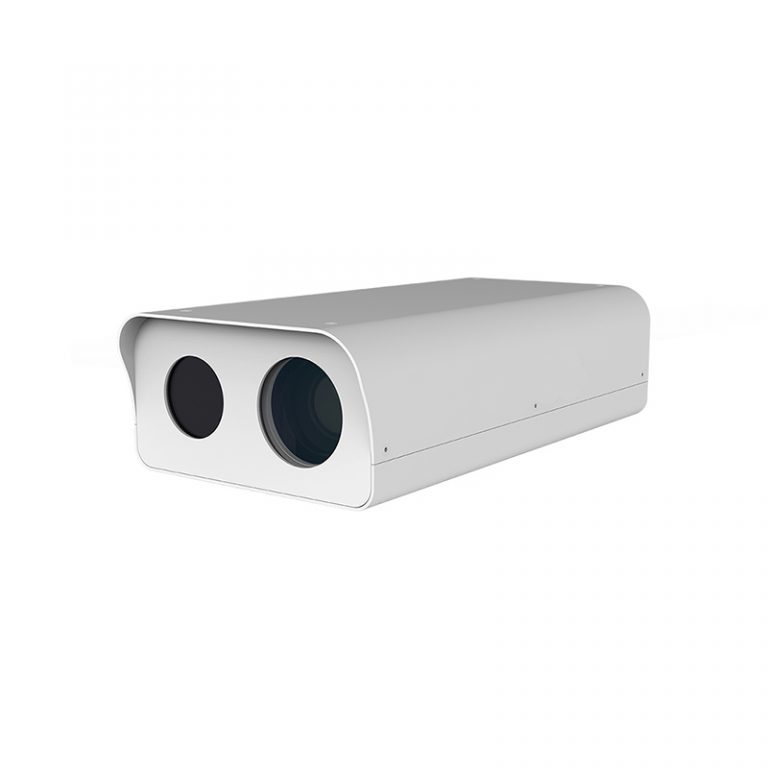

Bi-Spectrum Cabin Thermal Camer
-
-
Solutions
-
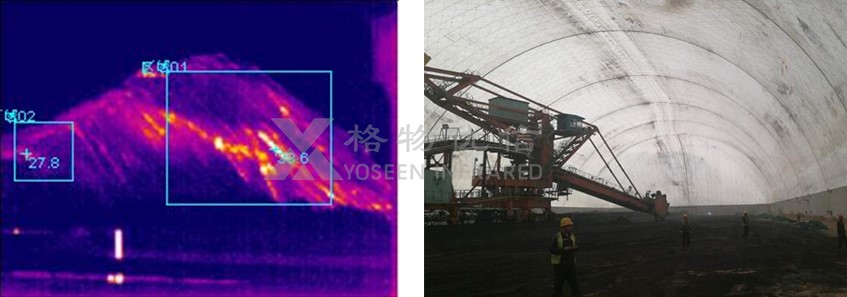
Prevention Solution of Coal Bun
-
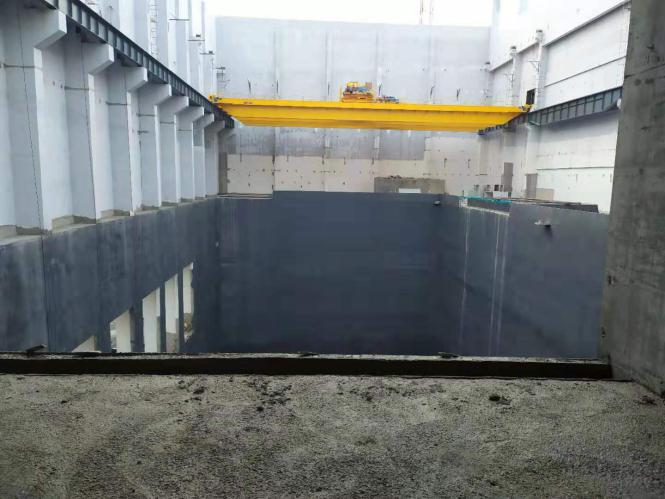

Garbage Power Station Dump Pit
-

Transformer Substation Thermal
-
Converter Station Infrared Ther
-

Electrolytic Aluminum Productio
-

Infrared Thermal Camera To Ensu
-

Infrared Thermal Camera Helps B
-

Factories Battery Warehouse The
-

Battery Warehouse Thermal Imagi
-
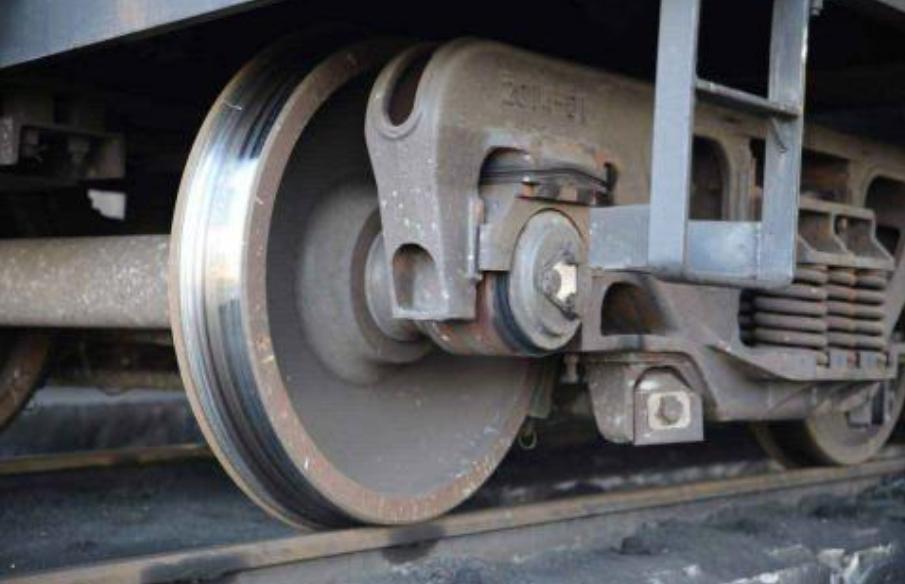

Train Wheel Hub Infrared Temper
-
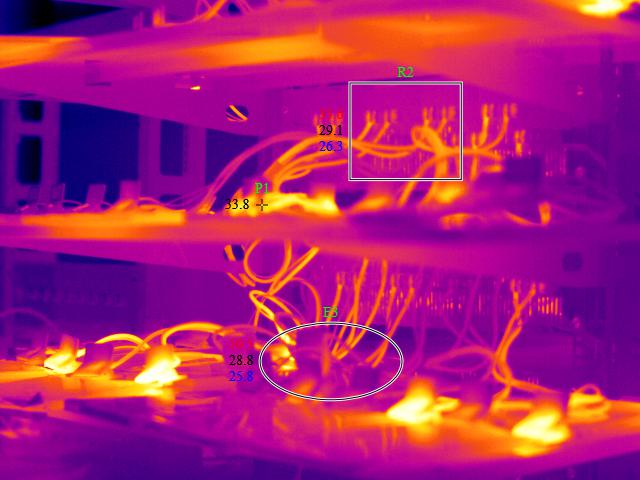

Power Distribution Cabinet Ther
-
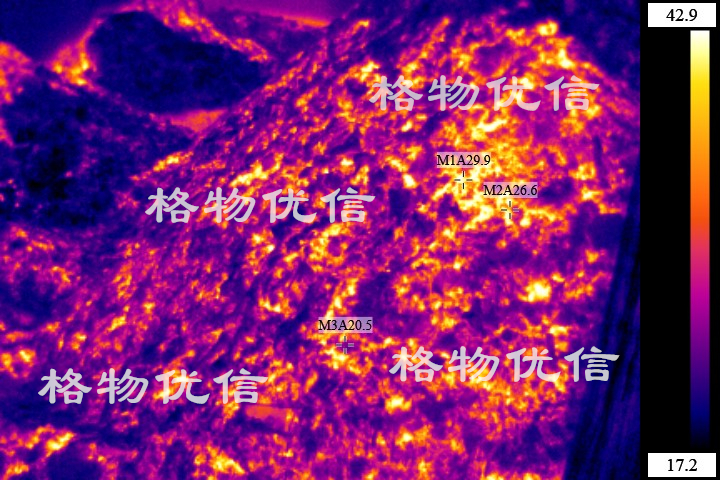
Intrinsically Safe Infrared the
-
- news
- about
- support
- contact



 鄂公网安备 ******号
鄂公网安备 ******号